This topic includes the following sections:
- Troubleshooting flowchart
- Step 1: Gather full information on the setup
- Step 2: Get a complete picture of the problem
- Step 3: Research the issue
- Step 4: Logging and other steps to isolate the problem
- Step Ω: Contacting Synergy/DE Developer Support
- Notes on connection problems
- Notes on performance issues
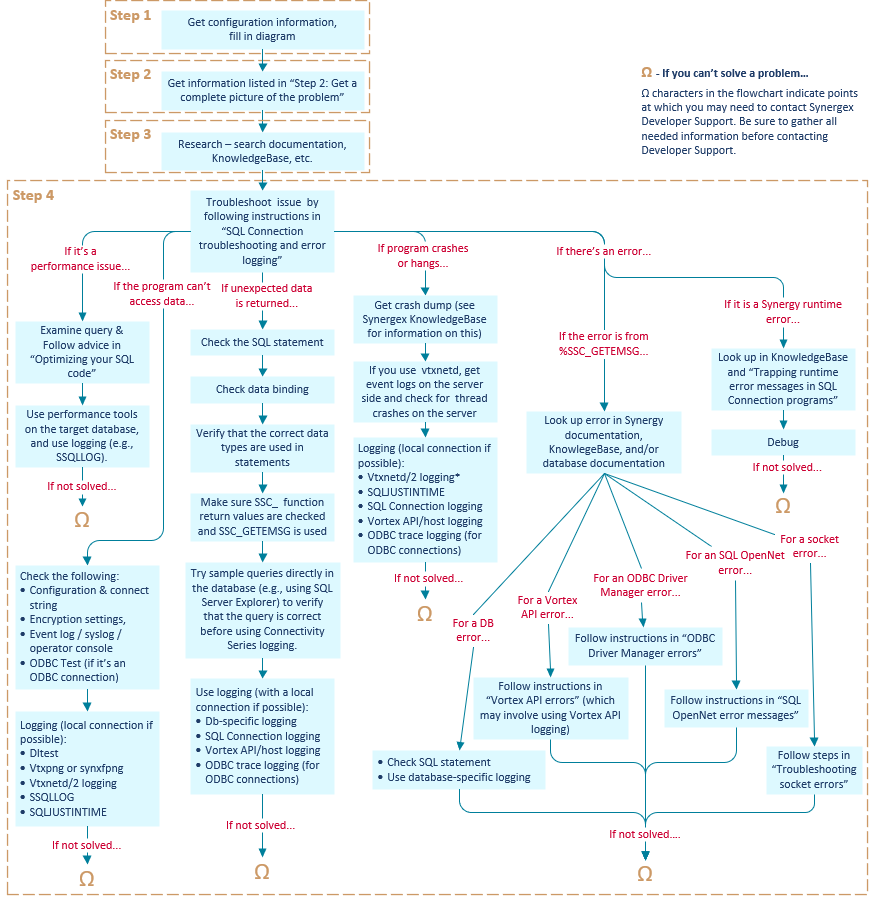
Troubleshooting flowchart
The flowchart below (figure 1) illustrates the general flow of troubleshooting steps for SQL Connection issues. The sections that follow provide details on the steps illustrated in the flowchart.
You won’t necessarily go through all the flowchart steps for every SQL Connection issue. You may discover the solution at any point in the process, and there can be situations where you’ll need to contact Synergy/DE Developer Support to resolve an issue (as the Ω characters in the flowchart indicate).
Step 1: Gather full information on the setup
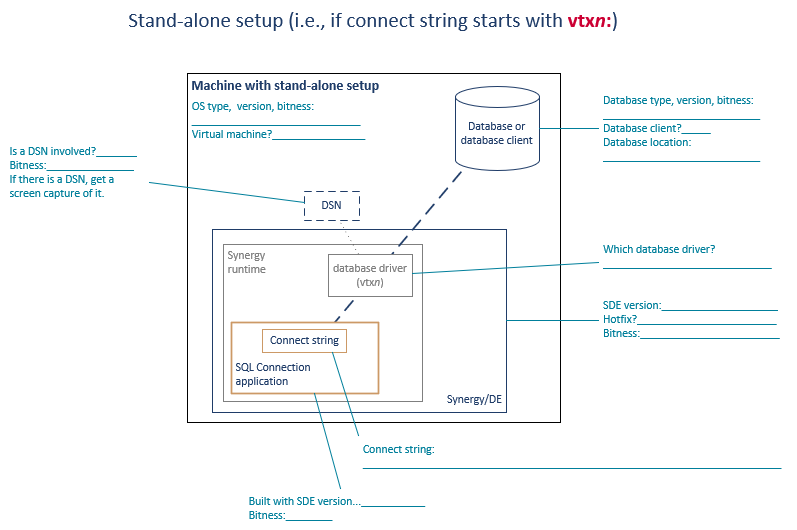
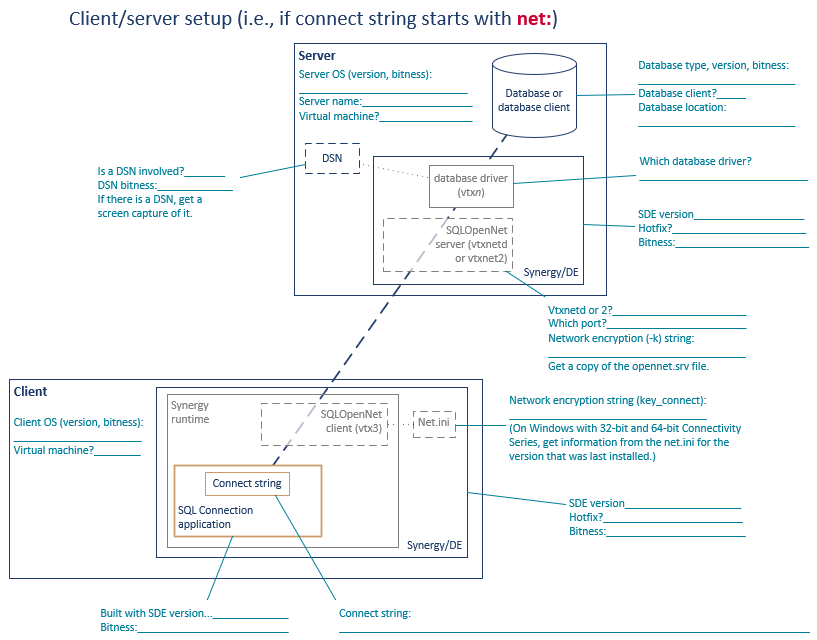
When you encounter an SQL Connection issue, start the troubleshooting process by making sure you have a complete picture of your SQL Connection configuration. Gather all the information mentioned in the applicable setup diagram below (stand-alone or client/server), and note any other configuration details that could be relevant.
Step 2: Get a complete picture of the problem
In addition to understanding the setup, you’ll need to bear in mind all details pertaining to the problem. Make sure you can answer the following questions, and be sure to gather any other information that could be relevant:
- What is the problem? Be sure to consider all the symptoms.
- Is there an error? If so, note the error mnemonic and text.
- Does the program terminate with a traceback? Is the error trapped?
- Is error information returned from %SSC_GETEMSG?
- What are the exact steps that led to the problem?
- At which statement did the error occur?
- What SQL statement was used?
- What changed (for example, code, data, or hardware) before the problem occurred?
- Can you consistently reproduce the problem?
Step 3: Research the issue
Once you have all the pertinent details about your SQL Connection configuration and circumstances surrounding the issue, find all published information related to the issue:
- If there’s an error, look it up in the SQL Connection error documentation (Error messages for SQL Connection) and in the Synergex KnowledgeBase. If the documentation or a KnowledgeBase article has troubleshooting information, use that to troubleshoot the problem.
- If the problem appeared after upgrading Synergy/DE, check release note entries for the current version for changes that might have led to the problem.
- For 10054/10061 errors and errors that contain “Connect:errno:error” or ”Recv:errno:error”, see Troubleshooting socket errors.
Step 4: Logging and other steps to isolate the problem
Next, follow the steps outlined in the “Step 4” area of the troubleshooting flowchart (figure 1), starting with steps outlined in SQL Connection troubleshooting and error logging and referring to the following sections in this topic (as applicable) for more information:
Additionally, keep the following in mind:
- To verify that the query is correct, try querying the database directly (e.g., with SQL Server Explorer) before using SQL Connection logging.
- Logging can cause a production environment to slow down, which can be a serious problem. If possible, it is generally best to reproduce an issue in an isolated test environment with a stand-alone configuration and then turn on logging in that environment.
Step Ω: Contacting Synergy/DE Developer Support
By the time you have arrived at an omega (Ω) character in the troubleshooting flowchart (figure 1), you’ve gathered all the relevant information, created a picture of the configuration, fully understood the problem, looked up error information, and generated any logs that could shed light on the issue. If you are still unable to solve the problem, it’s time to contact Synergy/DE Developer Support. See Contacting Synergy/DE Developer Support for more information.
Notes on connection problems
For database connection issues, do the following:
- Follow the applicable steps in the troubleshooting flowchart (figure 1) and SQL Connection troubleshooting and error logging.
- Refer to Components and configurations and Configuring Connectivity Series for more information on setting up SQL Connection to access a database.
- Examine the connect string in use to ensure it is constructed correctly. See Understanding connect strings and Building connect strings for details.
- Look up error messages in Error messages for SQL Connection and in the Synergex KnowledgeBase.
The following are some questions to consider. And note that may be necessary to involve network engineers or IT.
- Is the server running? You can use vtxping or synxfpng to test this, as well as vtxnetd/vtxnet2 logging. See SQL Connection troubleshooting and error logging, and note that vtxnetd/vtxnet2 logging is only appropriate in a development environment in a single-user scenario.
- What is the port/server name or IP address used for the connection?
- Do all the components have the correct bitness? (See figure 2 or figure 3.)
- How is the SQL OpenNet server started?
- The same encryption key should be used on both server and clients. Is it? (See vtxnetd and vtxnet2 programs and Setting options in net.ini.)
- Is a firewall enabled?
Notes on performance issues
For performance issues, follow the steps outlined in the troubleshooting flowchart (figure 1):
| 1. | Examine the SQL query in use to make sure it’s optimized. See Optimizing your SQL code for more information. |
| 2. | Use performance tools on the target database to debug the performance issue. You can also use logging, though it is not usually too helpful with performance issues. The exceptions are SSQLLOG logging and Vortex API logging. You can use SSQLLOG logging to see what operations were performed and then take this information to your database administrator. And you can use Vortex API logging to find out how well cursor usage is optimized. For more information, see SQL Connection troubleshooting and error logging. |