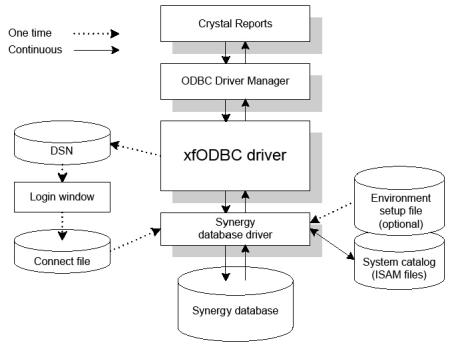
How third-party applications use xfODBC
When a user opens a 32-bit ODBC-enabled application, such as Crystal Reports, and accesses a Synergy database, the following components are called or read: ODBC Driver Manager, the xfODBC driver, your connect file, the system catalog, and the Synergy database.
The xfODBC process can be summarized by the following steps:
|
1.
|
The ODBC-enabled application (Crystal Reports in figure 1) makes a request to the ODBC Driver Manager, which loads the xfODBC driver and establishes an interface between the application and xfODBC. |
|
2.
|
xfODBC reads the data environment variables set in the environment setup file (optional). |
|
3.
|
xfODBC reads the information in the DSN. |
|
4.
|
xfODBC prompts the user for any information that’s missing from the DSN. |
|
5.
|
xfODBC reads the connect file and then locates the system catalog and data files. |
|
6.
|
xfODBC reads the system catalog for a road map of the Synergy database and then verifies the username and password against the registered users in the system catalog. |
|
7.
|
The ODBC-enabled application passes the SQL-based request to xfODBC, which then passes it to the Synergy database driver. |
|
8.
|
The Synergy database driver retrieves the requested data and passes it on to xfODBC, which “translates” it into a form recognized by the ODBC-enabled application. |